
- #QEMU SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS INSTALL#
- #QEMU SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS UPGRADE#
- #QEMU SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS FULL#
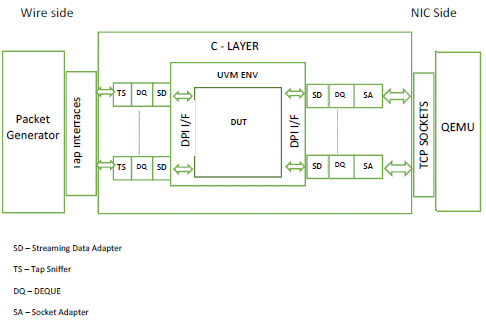
I am also using the NFS server to install the guest OS shown in Figure 2. In my test-bed, it is named ‘vm2’ to create the instance of an Ubuntu VM. Step 2: Install guest VM by clicking on ‘new’, then enter the name of your guest machine. A screenshot of the virt-manager graphical tool connected to the local hypervisor QEMU-KVM is shown in Figure 1. Step 1: Open the virtual machine manager graphical tool by typing virt-manager in a terminal.
The process of VM creation can be divided into the five steps that are listed below. The following command can be used to verify whether the system supports CPU virtualisation or not:
#QEMU SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS FULL#
Virtualisation extensions (Intel VT-x or AMD-V) are required for full virtualisation. An AMD processor with the AMD-V and the AMD64 virtualisation extensions.

An Intel processor with the Intel VT-x and Intel 64 virtualisation extensions for x86-based systems or.Host system requirements: The minimum host system requirement is 2GB of RAM plus additional RAM for VMs, 6GB disk space for the host plus the required disk space for the VMs. The system requirements for running virtual machines are highlighted below. System requirements to set up the VM migration environmentĪ virtualisation environment can be implemented using the KVM hypervisor. A word of caution, though – VM migration needs proper and detailed planning. Once you have the capability of moving virtual machines freely between different physical servers the benefits are countless.
#QEMU SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS UPGRADE#
Other benefits include an easy hardware/software upgrade process by moving the VM between different hypervisors. Once the virtual machines are migrated, you can power off the unused hypervisors. You can easily consolidate your virtual machines based on the load and usage to a smaller number of hypervisors during off-hours. Another important benefit is that it enables energy-saving, making it an environment-friendly process. A carefully designed virtualised environment provides the maximum possible uptime for any application. The most important benefit of VM live migration is increased uptime and reduced downtime. Server fault: Whenever there is a server fault, VMs are migrated from the faulty server to the target server. Hence, whenever there is a need for server maintenance, VMs from the source server are migrated to another data centre. Server maintenance: Any cloud data center’s maintenance is a continuous process. Server overload: When a source server is overloaded, a set of the VMs from this server is migrated to an underloaded server using any VM migration technique. VM migration is defined as: “The process of transferring a VM from a physical machine to a target data centre server to achieve load balancing, fault tolerance, server consolidation and server maintenance.”Ī cloud admin can execute VM migration in a cloud data center when any of the following happens: This article takes a quick look at the need for VM migration, its benefits, steps to develop an experimental test-bed for a cloud VM migration environment, and trends in virtualisation technology.Ĭloud computing inherits one of the key features provided by server virtualisation called virtual machine (VM) migration.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
